Shedding is something all cat owners experience. All furry cats shed, even those that are considered low-shedding or hypoallergenic breeds. So it’s totally normal to have cat hair all over your home. But if you notice increased shedding or your cat’s coat thinning, shedding can be a cause for concern. Increased shedding is often an indication of an underlying health problem that requires medical attention.
If you suspect your cat is shedding more than usual, it’s best to take them to the vet for a thorough check-up. Here are some reasons why cats shed and how to treat them.

8 reasons why cats shed so much
1. Seasonal hair loss
Many cat breeds are seasonal shedding breeds, meaning they shed heavily once or twice a year. Both single-coated and double-coated cats shed seasonally, but double-coated cats shed more easily and noticeably. Examples of seasonal shedding breeds include Maine Coons, Ragdolls, Persians, and Norwegian Forest Cats. These breeds typically shed their winter coat in the spring, so you’ll see them shedding the most during this time of year.

2. Allergies
Cats can be allergic to a variety of things in the environment, including pollen, dust mites, mold, etc. Some cats also have food allergies to animal proteins such as beef, chicken, and dairy products.
Allergies typically cause itchy, irritated skin, and an allergy-affected cat may lick and scratch themselves, resulting in increased shedding and hair loss, and a thinning coat.
3. Infections and Diseases
Cats can suffer from skin diseases and infections that can cause increased shedding. For example, irregular hair loss can be a sign of a bacterial or fungal infection. Ear infections can also cause hair loss around the ears due to scratching or self-inflicted injury.
Ringworm is a contagious fungal infection of the skin that usually causes patchy hair loss and thickened, scaly skin. Any cat can become infected, but it is more common in young, long-haired cats.

4. Stress
Just as humans shed hair due to stress, cats also begin shedding more when they are stressed. It is common for cats to shed more when they are stressed and groom themselves excessively. When the hair loss or self-trauma is due to behavioral causes, it is called psychogenic alopecia. To diagnose, your veterinarian must first rule out medical causes for the grooming.
There are many different factors that can cause stress in cats. A change in routine, boredom, loud noises, or moving to a new home can make your cat feel anxious and stressed. Stressed cats often exhibit other behaviors as well. Other common behaviors associated with stress include withdrawal or clinginess, changes in eating habits, elimination outside the litter box, and scratching and destroying furniture.
5. Aging
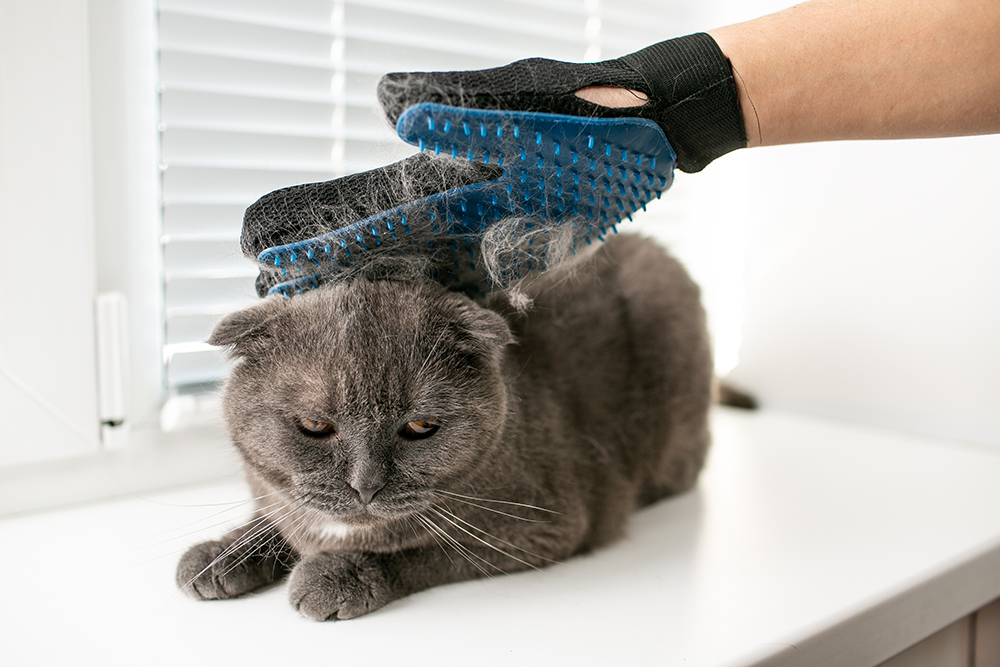
As your cat gets older, you may notice that they shed more. Older cats often stop grooming because it’s harder to reach certain parts of their body. So if you suddenly notice more hair shedding, it doesn’t necessarily mean your cat is shedding more; it could be because they’re no longer grooming themselves. Some older cats will appreciate a little help with more frequent brushing. Brushing removes dead hair from their fur, reducing shedding and preventing tangles.

6. Parasites
Parasitic infestations are also a common cause of increased hair loss and balding in cats. Fleas and mites that live on the skin and fur can cause itching and irritation. Some cats are also allergic to flea saliva, causing them to react more violently to flea bites.
As the infection spreads, your cat will continue to lick and scratch its skin, causing increased hair loss.
7. Nutritional deficiencies
Diet plays a vital role in maintaining healthy skin and coat. In addition to adverse reactions to food, nutritional deficiencies can also cause skin diseases and lead to increased hair loss and shedding. Cats need to consume a complete and balanced diet every day that contains all the essential nutrients they need to stay healthy. Cats whose nutritional needs are not consistently met will inevitably become malnourished and be at increased risk of developing health complications, including poor quality, dry and brittle coats, which can lead to hair loss.
A range of nutrients are needed to maintain healthy skin and fur, including adequate protein and fat levels, omega fatty acids, vitamin A and biotin.

8. Medication
Some medications have a side effect of causing hair loss. Certain topical medications, such as parasitic medications, may cause your cat to lose hair around the injection site. Steroids, especially high doses, are also known to cause hair loss in some cats. Rarely, your cat may lose hair around the injection site after a vaccination.

Preventing excessive shedding in cats
Although all cats shed, it’s still important to keep a close eye on them and make sure their shedding is healthy and normal.
One of the best ways to prevent your cat from shedding too much is to keep up with its annual vet checkups. Taking your cat to the vet annually will help keep your cat happy and healthy and allow your vet to detect any potential risks to your cat’s health. If shedding is accompanied by other signs such as thinning fur, bald patches, itching or skin rashes, be sure to consult your vet. Your vet will be able to determine if your cat’s shedding is normal or if further measures are needed.
Another way to manage shedding is to establish a grooming routine for your cat. This includes regular brushing and, depending on the cat, occasional bathing. Brushing helps remove loose and dead hair from your cat’s fur, reducing the amount of hair that ends up on carpets and furniture. While brushing your cat, you can check for unusual colors, skin problems, and signs of parasites.
Finally, helping your cat maintain a healthy lifestyle can help keep shedding to a normal level. Stress can lead to shedding, so it’s important to make sure your home is a fun and safe environment for your cat. Make sure your cat has plenty of safe places to hide and rest, and provide them with fun toys to keep them from getting bored.
Creating a daily routine can be especially helpful for anxious cats, as they’ll feel reassured and more at ease knowing what to expect.

Conclusion
Cats can shed excessively for a variety of reasons. Excessive shedding, especially if the coat is thinning or there are areas of hair loss, is often a sign of a larger health problem that requires veterinary attention. However, some cat breeds shed more than others. Luckily, you can take proactive steps to make shedding more manageable. Establishing a consistent grooming routine can help reduce shedding in your home and keep your cat’s coat healthy and shiny.
Featured image credit: New Africa, Shutterstock




